
Antioxidants are artificial or natural compounds that may avert or slow some kinds of cell damage. Antioxidants possess vitamins C and E, selenium, and carotenoids (including beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin). Vegetables, fruits, and spices are suitable bases for antioxidants; however, analysis has not established all other antioxidant supplements are healthy in controlling disorders.
Read on to learn why antioxidants are a vital part of any healthy lifestyle.
Key Points Regarding Antioxidants
A piece of good evidence is that eating plenty of vegetables and fruits is healthful, and authorized U.S. Management policy recommends people eat more.
The study has shown that people who take more vegetables and fruits have decreased risks of several ailments; however, it is not explicit whether these results are associated with the number of antioxidants in vegetables and fruits, other elements of these foods, to other factors in your diet, or to different lifestyle options.
Strict scientific investigations involving over 100,000 people have tested whether antioxidant supplements can aid in preventing chronic diseases like cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and cataracts. In most cases, antioxidants did not lower the growing risks in these conditions.
Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants
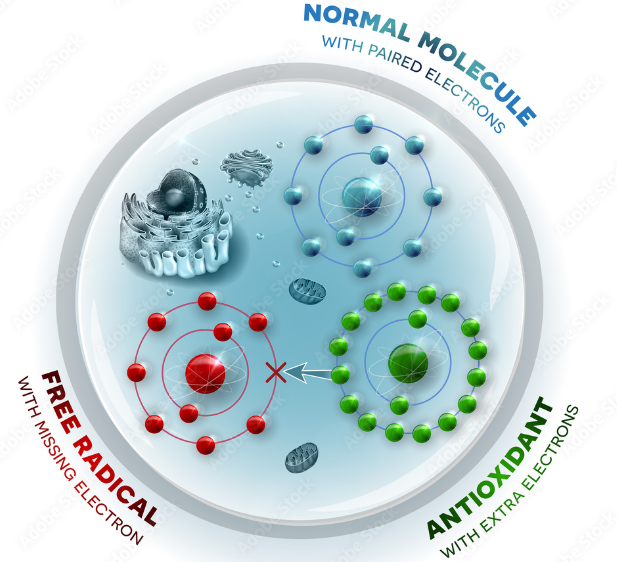
Free radicals are volatile molecules naturally formed when you exercise and when your body transforms food into energy. They can induce “oxidative stress,” triggering cell damage. Oxidative stress plays a role in a host of diseases, including:
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Eye diseases (cataracts and age-related macular degeneration)
Your body can also be vulnerable to free radicals from various environmental pollutants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and sunlight.
Antioxidant molecules have been shown to neutralize oxidative stress in lab experiments (for example, in cells or animal studies). However, there is an ongoing debate as to whether ingesting large amounts of antioxidants in supplement form really benefits health. There is also some concern that excessive eating of antioxidant supplements may be deadly.
Official U.S. State policy instructs people to eat more vegetables and fruits. Veg and fruits are healthy foods and rich sources of antioxidants. Concerns about the safety of any amounts of antioxidants in food have not been presented.
Intake of Antioxidant Supplements in the U.S.
A 2009 study showing a report from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey calculated how much antioxidants adults in the U.S. get from foods and supplements. Supplements contributed to good amounts of vitamin C, vitamin E, alpha- and beta-carotene, and selenium consumption.
What are antioxidants, and what do they do for your body?
Let’s talk science – basically, antioxidants are substances that can help to avert or delay the damage of cells. They act as scavenging agents, harmful molecules called free radicals, which can wound cells and contribute to developing diseases as a result.
It’s significant to note that your body innately produces free radicals due to normal metabolic processes, but they can also be induced by openness to environmental toxins, such as cigarette smoke and UV radiation!
How can I improve the level of antioxidants in my body?
Antioxidants can be found in a host of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, spices, and nuts! Eating foods that are rich in antioxidants is a great way to naturally guard your body against free radicals, as this activity enhances the levels of antioxidants in your blood. By improving your diet with healthy foods, you are enabling your body to combat potentially harmful oxidative stress.
Want to uncover some of the finest sources of antioxidants and how to include them in your diet? You’ve come to the right place!
Foods Wealthy in Antioxidants

You don’t need to go here and there to refill your diet with antioxidants – they happen to occur in packs of different foods you can choose from your nearest supermarket. Here are some of our leading antioxidant foods that you could readily include in your weekly bags:
- Beetroot – Beetroot is a nutritional powerhouse loaded with vitamins and minerals! It is an excellent fiber and vitamin C source, and it also holds essential nutrients like potassium and folic acid.
- Pecans are a fine source of several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E, magnesium, and zinc. They even possess plant sterols, which may help to lower cholesterol levels!
- Blueberries – Blueberries are a tasty and healthy addition to any diet. Being a good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, blueberries are also low in calories and fat.
- Strawberries – Strawberries are fibrous, delectable, and nutritious fruits. These delightful red fruits are not only a joy to eat, but they also are a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, and folic acid. They also have ellagic acid, which has been established to have cancer-fighting effects.
- Turmeric – Turmeric is a potent antioxidant. It has also been shown to lower cholesterol and triglycerides in people with clogged arteries and may regulate blood pressure. Antioxidants in turmeric may also decrease the risk of cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration.
Does none of the above tickle your taste? What is the best way to take antioxidants – in supplement form or via food? Try testing with Turmeric curcumin supplements for an antioxidant increase with ginger & black pepper!
Foods are exploding with nutrients and fibers, all of which play a noteworthy role in how our bodies absorb antioxidants. With this in mind, supplements may instantly affect. The most eminent antioxidant vitamins are vitamin C, E, and beta-carotene – but you’ll find most of these nutrients in foods that are radiant in color!
Besides supplements, slotting a homemade turmeric shot made from refined, unpasteurized elements into your daily routine is a speedy and easy way to ensure that you are getting your antioxidant fix without holding to discover the time to eat several bowls of fruit!
Remember – you can get all the nutrition you need from your consumption!
What the Science Says
Several years of dietary research indicated that consuming more significant amounts of antioxidant-rich foods might help defend against diseases. Because of these effects, there has been a lot of research on antioxidant supplements. Strict trials of antioxidant supplements in many people have not found that high doses control the disease. This section defines the preliminary research spottings, the results of the clinical trials, and potential grounds for the differences in study results.
Why are Antioxidant Supplements not working for you?
Many clinical studies of antioxidant supplements have not discovered considerable health benefits. Researchers have indicated several reasons for this; here are the following:
- The beneficial health impacts of a diet rich in veg and fruits or other antioxidant-rich foods could even be caused by other compounds in the same foods, other dietary aspects, or other lifestyle selections than antioxidants.
- The effects of the high doses of antioxidants used in supplementation studies may differ from those of the smaller amounts ingested in foods.
- Dissimilarities in the chemical composition of antioxidants in foods versus those in supplements may affect their results. For instance, eight chemical forms of vitamin E are present in foods. Vitamin E supplements generally have only one of these forms—alpha-tocopherol. Alpha-tocopherol also has been used in virtually all research studies on vitamin E.
- For some diseases, specific antioxidants could be more effective than the ones that have been trialed. For example, to prevent eye infections, antioxidants present in the eye, such as lutein, may be more healthy than those not found in the eye, like beta-carotene.
- The connection between free radicals and health may be more complex than previously assumed. In some cases, free radicals may actually be beneficial rather than harmful, and dismissing them may be disfavored.
Safety First
- High-dose antioxidant supplements may be detrimental in some cases. For example, some studies’ effects have related high-dose beta-carotene supplements to a raised risk of lung cancer in smokers and high-dose vitamin E supplements to inflated chances of hemorrhagic stroke (stroke due to brain bleeding) and prostate cancer.
- Likewise, other dietary supplements and antioxidant supplements may react with certain medicines. For example, vitamin E supplements may improve the bleeding risk in those taking anticoagulant drugs (“blood thinners”). There is clashing evidence on the impacts of taking these supplements during cancer therapy.
- Some studies indicate that this may be useful, but others propose that it may be dangerous. The National Cancer Institute suggests those who are being treated for cancer talk with their healthcare provider before eating supplements.
What If You Are Looking for Antioxidant Supplements
- Do not use these supplements to substitute a healthy diet or traditional medical care or as a reason to delay seeing a health care provider regarding a medical problem.
- If you have age-related macular degeneration, speak to your health physician to decide whether supplements of the type used in the AREDS study are right for you.
- Preferably, get data from reliable sources if you are assuming a dietary supplement. Remember that nutritional supplements may interact with prescriptions or other supplements and include ingredients not listed on the label. Your doctor can advise you.
- If you are pregnant, nursing a child, or considering giving your kids a dietary supplement, it is essential to consult your (or your child’s) healthcare provider. Also, tell them about any complementary health strategies you use.
And you can get your antioxidant fix by adopting some healthy tweaks to your diet! Pretty impressive, right?
Well, it turns out that antioxidants may play a role in slowing the onset of some chronic conditions, such as heart disease, and could help with cancer prevention. They may also provide nutrients to help support normal cognitive processes and memory.
Taiba Tariq
Taiba Tariq is a healthcare nutrition hobbyist, enthusiastic about researching healthcare & skincare news while analyzing the latest and science-backed evidence about nutrition, skin care, and supplements. She wants to help people regain their beauty, health, and well-being through natural means.
all author posts




